
Here are some things that you do on the internet and how much bandwidth (and data) it uses up: You can also visit Numion and play with their calculator. To give you a better idea how much bigger or small each unit of speed (bandwidth) is, here is a handy conversion chart. Gigabits are hardly used for internet plans, and the costs make them unpractical for families and small businesses. Megabytes aren’t usually used in (residential) internet plans. This is the most common unit of speed used. The difference between the two is how the “b” is written in the abbreviation M bps = megabits and M Bps = megabytes. Some people confuse this with mega bytes. This is used when talking about dialup (56k for example) and low speed DSL. Below that I’ve outlined a basic conversion guide and a rough idea as to how big each piece of data you consume is. These are the abbreviations for the amount of data that is being sent per second. Mbps, MBps, kbps, Gbps what does all of this mean? What is kbps, mbps, MBps and gbps?Īnother confusing aspect of shopping for internet based on speeds are all the terms or abbreviations being used. However, real “internet speed” has to do with latency and that topic is outside the scope of this particular article. It’s more efficient, making your internet perceptually faster, not technically faster.Īll of that said, there isn’t just one internet speed. Your data is just transferred to you at a faster rate because more data can be sent at the same time. What’s important to note here, and this confuses a lot of people, is that your internet isn’t any faster from 1 Mbps to 5 Mbps, or however much bandwidth your connection has.
BANDWIDTH VS SPEED DOWNLOAD
In this example, you can download 5 images with the wider bandwidth in the same time you could 1 with the narrower bandwidth. More bandwidth means that you’ll receive more data at the same time. How fast will you receive your image? 1 second. Now let’s say that you have a 5 Mbps (bandwidth) connection, or a 5 lane freeway.
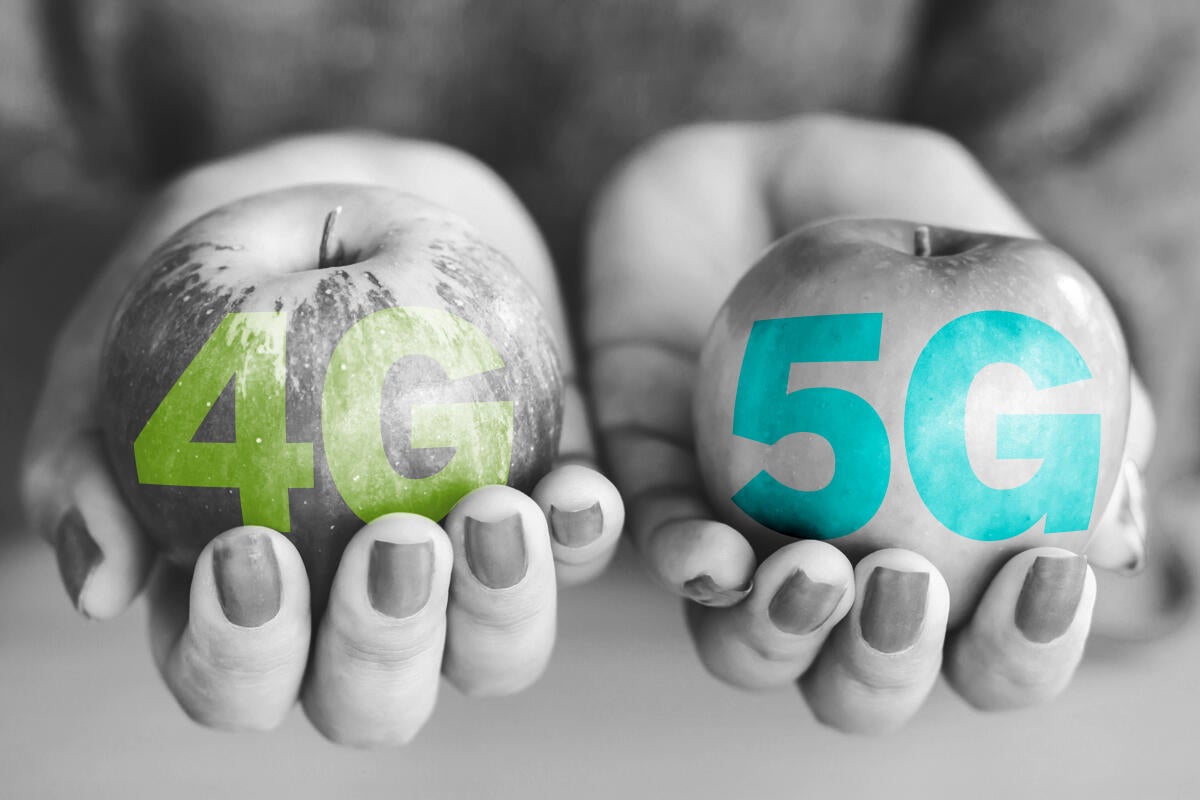

So if you had a bandwidth of 1 Mbps (1 lane freeway) it would take you roughly 5 seconds to download the image. And let’s say that you were trying to download an image, which is 5 Mb in size. In other words, say 1 Mbps is the equivalent to a 1 lane freeway. All cars (data) travel at the same speed, so to get more data from the internet to your computer faster, the freeway needs to be wider. The best way to explain (and understand) how bandwidth (and your internet speed) works is by using an analogy. For example, 5 Mbps would mean that you can receive up to 5 megabits of data per second. Bandwidth is the amount of data that can be sent to you, usually measured in seconds. Instead, internet speed is your (allocated) bandwidth. It’s not like a car or motorcycle where you can measure how fast it goes in miles per hour (mph). Internet speed, the number they give you (5 Mbps, for example), has nothing to do with how fast your internet works.
BANDWIDTH VS SPEED WINDOWS
Want the fastest internet speed at an affordable price? Find the best provider based on your needs:Įach page will open in a new windows so that you can finish reading this guide. Reach out now, and get a plan that fits your needs. We’ve collected phone numbers for the biggest ISP’s within the US. What is the difference between upload and download speeds?.To help you out, though, this article will answer the following questions:

But it’s the internet service providers biggest selling point, so speed must be important… right? They don’t know what internet speed is, how it works and why they should pay extra for more of it. Lots of people are confused with internet speed. Does internet speed confuse you? Do you scratch your head when you hear the words megabits, bandwidth or latency?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
